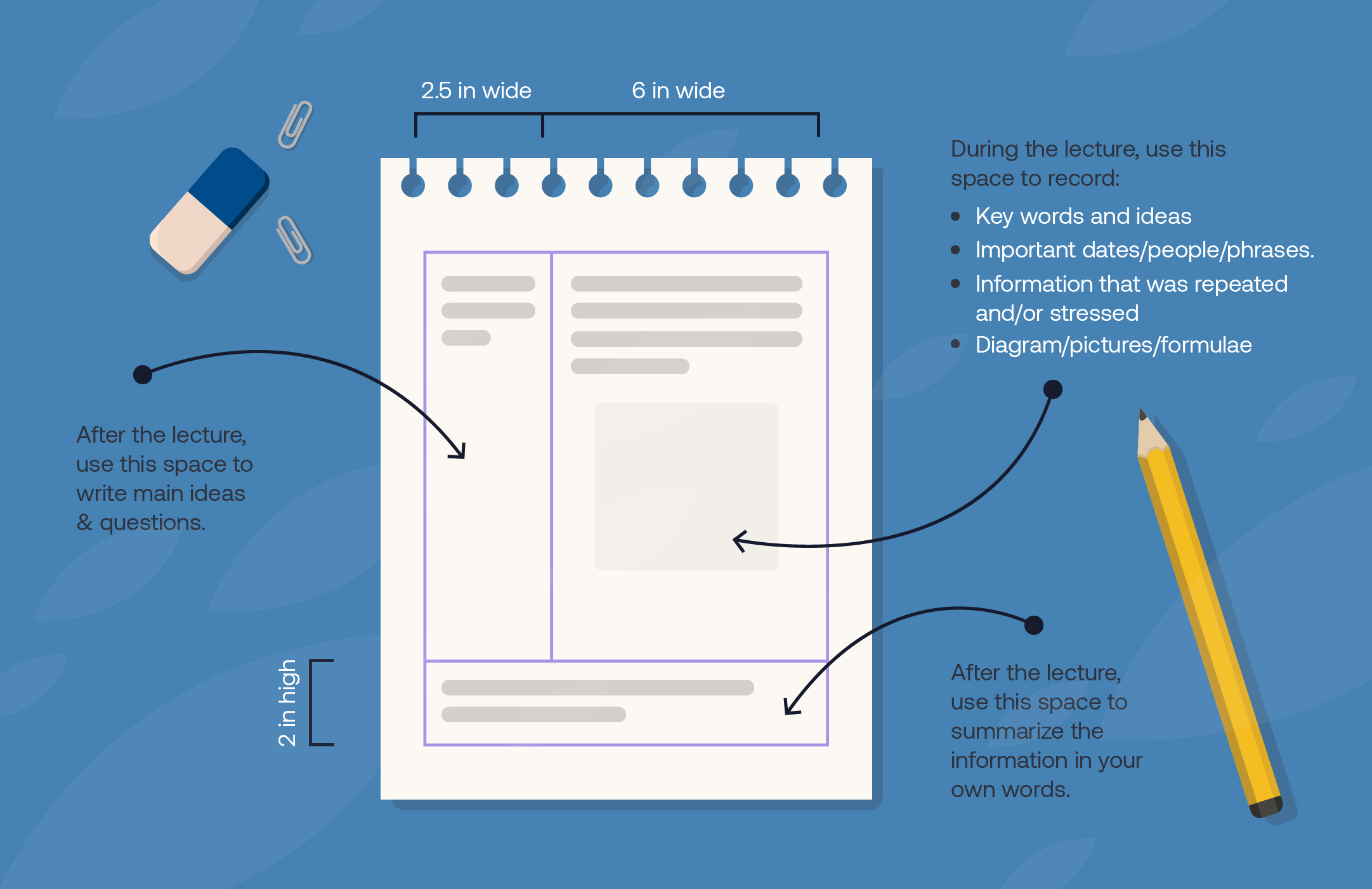
The Cornell Note-taking system
Using Cornell notes
Consider using the Cornell notes format for note-taking, which makes it easier to pull key ideas out of your notes, and use your them for review.
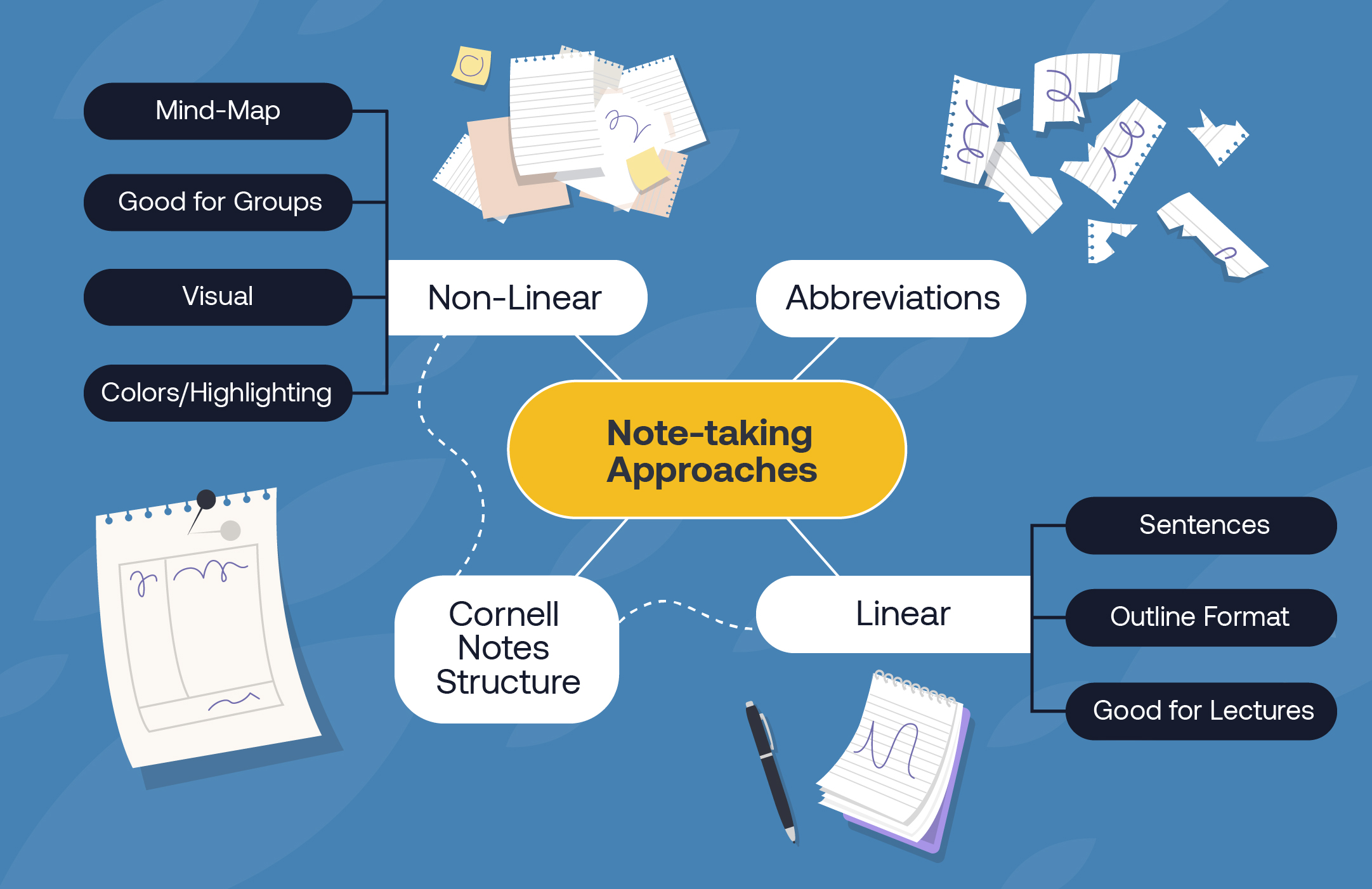
Other note-taking methods
Using dashes or indents is a good way to take notes because you are able to quickly create a hierarchy such as a main idea, a supporting point, and a sub-point.
Many note takers use shortened versions of words to save time. Notice the shortened words information (info), organized (orgd), hierarchy (hierchy), sub-points (subpts), with (w), and more.
Outline format:
• Info orgd in hierachy
• Main idea, then subpoints (deductive)
• Inductive; subpoints build to main pt
• Use dashes 4 speed, edit ltr
• Disadv: hard to use w fast lctre
This non-linear note-taking method can show relationships among ideas and information. In this example, a central idea is connected to supporting ideas:
Start a new line for every new thought, fact, or topic. This is a good method when a lecturer is moving quickly. After the lecture, review your notes and organize them further if needed.
Sentence method:
• Bttr 4 fast-mvg lectr
• Can orgze later
• D/n show relshp of ideas
Use this when the presenter provides information in a patterned way.
| METHOD | TYPE | ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outline | Linear | easy 2 see main ideas | hard in fast-mvg lectr |
| Map | Non-linear | shows rel’shps | hard in fast-mvg lectr |
| Chart | Linear | organizes info | only use 4 v strctrd presentn |
| Sentence | somewhat linear | fast | notes less orgzd |
During or after note-taking, organize your notes using questions, answers, and supporting evidence. For example, if you were listening to a lecture on note-taking, you might write notes like this:
Q: best method for note-taking?
A: handwrite, summarize & write concepts in own words
Evidence: June 2014 article, Psychological Science, Mueller & Oppenheimer: students who handwrite & summarize remember better
Some common abbreviations
| – minus, without & and, plus, with ∵ due to, because of / per (10 ft/in for 10 feet per inch) ? uncertain, possibly, unproven < is less than, is smaller than ≠ does not equal, is not the same as, does not result in = equals, is the same as, results in > is greater than, is larger than ≈ is approximately equal to, is similar to ↑ increase, rise, growth ⇈ rapid increase therefore, thus → leads on to, produces, causes ↓ decrease, fall, shrinkage ⇊ rapid decrease b4 before bc because C century (e.g. C19 for nineteenth century) … etc. and so on ca circa, about, around cf. compared to, by comparison with ch chapter diff difference |
d/n does not e.g. for example esp especially etc et cetera, so forth ex example i.e. that is, in other words K a thousand (500K = 500,000) M a million ($6m = 6,000,000 dollars) p page ppl people Q/A question answer re regarding, about ref reference s/o someone s/th something v. very vs versus, as opposed to w/ with (something) w/o without x no, not, incorrect xx definitely not, disproved yr year |